How to Write a Literature Review
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips Particularly in the fields of research, theses, dissertations, and scholarly publications, a literature review is a crucial component of academic writing.
It entails the methodical analysis and interpretation of prior research, theories, procedures, and findings that are pertinent to a given subject. Writing a literature review identifies gaps, trends, and areas for additional research in addition to helping place your work within the framework of previous studies.
What is a Literature Review?
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips A literature review serves as a synthesis of existing research on a given topic. Its purpose is to:
- Summarize and analyze what has been done in the field.
- Identify gaps and areas that require further investigation.
- Establish a theoretical framework for your research.
- Highlight methodologies and trends in previous studies.
Why is a Literature Review Important?
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips A well-written literature review serves several crucial purposes:
- Provides context for your study: It shows the background and relevance of your research, justifying why your study is needed.
- Identifies gaps: By highlighting existing research, you can spot areas where little or no research has been done, allowing you to make a unique contribution.
- Evaluates methodologies: Understanding the methods used in existing studies helps you design your own research more effectively.
- Synthesizes knowledge: It brings together various findings to present a broader picture of the current state of knowledge on your topic.
Steps to Writing a Literature Review
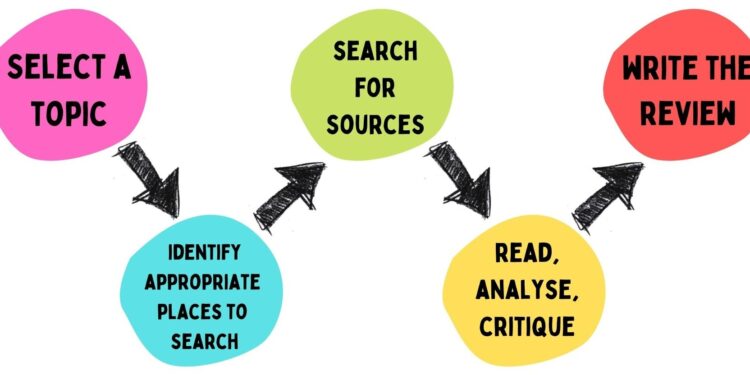
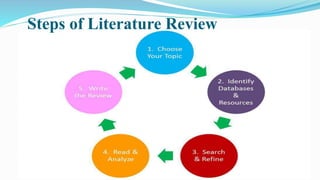
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips Writing a literature review involves several steps, from gathering sources to presenting your findings. Let’s walk through each of these steps systematically.
1. Define Your Research Question or Objective
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips Before you start searching for literature, it’s important to clarify your research question or the objective of your review.
A well-defined question will guide the scope of your literature review and help you narrow down the sources to consider. For example:
- What is the impact of artificial intelligence on healthcare?
- How do social media platforms influence consumer behavior?
2. Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Search
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips The next step is to conduct a thorough search for relevant literature. Sources to consider include:
- Academic databases: Google Scholar, JSTOR, PubMed, Scopus, and others.
- Books and book chapters: University libraries and digital books.
- Conference papers: Emerging research often presented at conferences.
- Theses and dissertations: Many universities publish graduate theses which can be rich sources of information.
When searching, make sure to use relevant keywords and filters to narrow down results to the most relevant and up-to-date publications. Be aware of the type of sources you choose (peer-reviewed, credible, and relevant).
3. Evaluate and Select Relevant Sources
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips Once you’ve gathered a collection of sources, evaluate each one for relevance, credibility, and quality. Criteria to consider include:
- Relevance to your research question.
- Credibility: Prefer peer-reviewed journals, books by respected authors, and sources from reputable academic institutions.
- Publication date: Prefer recent studies, although seminal works are still relevant in some cases.
4. Organize the Literature
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips The next step is to organize the literature in a logical structure. This will depend on your approach to the review:
- Chronological: Organizing studies based on their publication dates. This approach highlights the evolution of the field.
- Thematic: Grouping literature into themes or topics. This method is useful when a topic has various subtopics or perspectives.
- Methodological: Organizing studies based on the research methods used. This is ideal if you’re comparing different approaches to the same issue.
- Theoretical: Grouping studies based on the theories or models they employ.
5. Synthesize the Literature
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips Rather than simply summarizing each source, your goal is to synthesize the information. This involves:
- Analyzing the findings: Identify patterns, trends, and contradictions across the literature.
- Comparing studies: Discuss how different studies support or challenge each other. Point out areas where consensus exists or where debate is ongoing.
- Identifying gaps: Highlight areas of research that need further exploration or unresolved questions.
- Providing critical analysis: Critique methodologies, results, and interpretations. Discuss any limitations or biases in the studies reviewed.
6. Structure Your Literature Review
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips A literature review generally follows a standard structure, which includes:
- Introduction: A brief overview of the topic and the scope of the review. State your research question or objective.
- Body: The main body of the review should be organized into sections based on your chosen structure (chronological, thematic, methodological, etc.). Each section should highlight relevant studies and synthesize the findings.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main findings, discuss gaps in the literature, and emphasize how your research will contribute to the field.
7. Edit and Revise
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips After completing the first draft, review your work for clarity, coherence, and flow. Check for any redundancy or irrelevant information. Ensure that citations and references are properly formatted according to the required citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
Tips for Writing an Effective Literature Review
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips Here are some practical tips to make your literature review stand out:
- Be selective with sources: Choose only the most relevant and high-quality sources for your review.
- Stay focused: Keep your review focused on your research question and avoid diverging into unrelated areas.
- Be critical: Don’t just summarize studies; critically analyze them, pointing out strengths, weaknesses, and limitations.
- Use direct quotes sparingly: Paraphrase information where possible, and use direct quotes only when necessary.
- Maintain coherence: Ensure the review flows logically from one section to the next, and always tie back the literature to your research question.

Conclusion
How To Write A Literature Review: Examples And Tips To sum up, composing a literature review is a crucial and frequently difficult assignment in scholarly study.
Reviewing, synthesizing, and critically analyzing the body of existing information calls for an organized strategy. A well-structured and written literature review establishes the groundwork for your own study and helps place it in the perspective of previous findings.
You may make sure that your literature review is thorough, understandable, and perceptive by adhering to a methodical procedure from formulating your research topic to synthesizing the literature.
Always keep in mind that a literature review is more than just a synopsis of earlier research; it is a crucial component of your study that draws attention to gaps, arguments, and the importance of your work in the scholarly discourse.
(FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between a literature review and a research paper?
A1: A literature review focuses on summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a topic. A research paper, on the other hand, presents original research findings and contributes new knowledge to the field.
Q2: How long should a literature review be?
A2: The length of a literature review varies depending on the assignment or publication requirements. For a research paper, it could be between 3-10 pages, while for a thesis or dissertation, it could range from 20 to 50 pages.
Q3: How do I avoid plagiarism in my literature review?
A3: To avoid plagiarism, always cite your sources accurately using the required citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Paraphrase properly and use quotations only when necessary.
Q4: How do I decide which studies to include in my literature review?
A4: Choose studies that are relevant to your research question, published in reputable journals, and have solid methodologies. Consider both recent and seminal works that have shaped the field.
Q5: Can I write a literature review on my own research?
A5: Yes, you can write a literature review on your own research. This is often part of a dissertation or thesis where you review the literature related to the research question you’re investigating.
Q6: What are the common mistakes to avoid when writing a literature review?
A6: Common mistakes include summarizing instead of synthesizing, lacking a clear structure, using outdated sources, and not critically analyzing the literature. Avoid redundancy and make sure the review is directly tied to your research question.
Q7: How do I manage large amounts of literature?
A7: Use citation management tools like Zotero, Mendeley, or EndNote to organize your sources. Creating annotated bibliographies for each source can also help you track key points and findings.
Read More :