Explain American Romanticism with examples
American Romanticism was a literary and artistic movement that emerged in the early 19th century and reached its peak during the mid-1800s. It was a reaction against the rationalism and order of the Enlightenment period, and it celebrated individualism, emotion, and the connection between humanity and nature. American Romanticism was a diverse and multifaceted movement, encompassing various forms of art and literature, and it left a lasting impact on American culture.
American Romanticism: A Historical Context and Overview
American Romanticism can be understood within its historical context, which was marked by significant social, political, and cultural changes. The late 18th and early 19th centuries witnessed the birth of a new nation, the United States of America, which was founded on Enlightenment ideals such as reason, democracy, and individual rights. However, as the 19th century unfolded, the nation grappled with issues like industrialization, westward expansion, and the rise of a market economy. These developments brought about both economic prosperity and social upheaval, leading to a search for identity and meaning.
Romanticism, which sought to explore the natural, spiritual, and emotional dimensions of human existence, arose in reaction to these changes. It valued each person’s inner world, intuition, and creativity and promoted a strong relationship with the natural environment. Let’s look at the key characteristics of American Romanticism and provide examples to illustrate them.
Characteristics of American Romanticism
- Emphasis on Emotion and Imagination: American Romanticism placed a strong emphasis on the power of emotion and the imagination. It rejected the cold rationalism of the Enlightenment and championed the intuitive and emotional aspects of human experience. One notable example of this characteristic can be found in the poetry of Emily Dickinson. In her poem “Hope is the thing with feathers,” she describes hope as a bird that perches in the soul and sings sweetly, portraying it as an emotional and imaginative force:“Hope is the thing with feathers That perches in the soul, And sings the tune without the words, And never stops at all.”
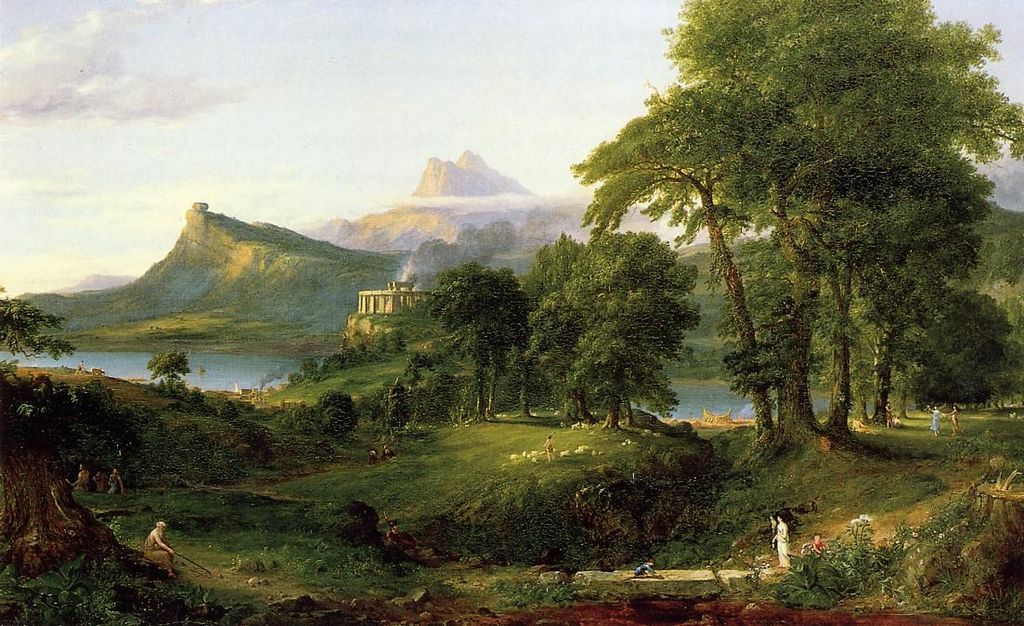
- Celebration of Individualism: Romanticism celebrated the uniqueness and individuality of each person. This was particularly evident in the writings of Ralph Waldo Emerson, who encouraged people to trust their own intuition and follow their individual paths. In his essay “Self-Reliance,” Emerson famously stated, “Trust thyself: every heart vibrates to that iron string.” He urged individuals to follow their own instincts and not conform to societal expectations.
- Connection with Nature: American Romanticism highlighted the deep connection between humanity and nature. Nature was often portrayed as a source of inspiration, solace, and spiritual insight. One of the most iconic works in this regard is Henry David Thoreau’s “Walden.” In this book, Thoreau describes his experience living in a cabin by Walden Pond, where he sought to live a simple and deliberate life in harmony with nature. He wrote, “I went to the woods because I wished to live deliberately, to front only the essential facts of life.”
- Exploration of the Supernatural and the Mysterious: American Romantics were fascinated by the mysterious and the supernatural. This can be seen in the works of Edgar Allan Poe, who is known for his gothic tales and poems. In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Poe creates an eerie and mysterious atmosphere as he tells the story of the Usher family and their ancestral home, which seems to be haunted by a supernatural presence.
- Critique of Industrialization and Urbanization: As America underwent rapid industrialization and urbanization, Romantic writers often criticized the negative impacts of these developments on society and the environment. Nathaniel Hawthorne’s “The Blithedale Romance” is a novel that explores the consequences of industrialization and the loss of a simpler, more natural way of life.
- Fascination with the Past: American Romantics were drawn to the past, particularly the colonial and frontier periods of American history. They often idealized these earlier times as more authentic and filled with untamed wilderness. James Fenimore Cooper’s “The Last of the Mohicans” is a classic example of this fascination with the past, as it depicts the adventures of frontiersmen and Native Americans during the French and Indian War.
- Exploration of the Sublime: The concept of the sublime, which refers to the overwhelming and awe-inspiring aspects of nature and the universe, was a common theme in American Romanticism. This can be seen in the paintings of the Hudson River School, a group of artists who sought to capture the grandeur of the American landscape. One of the most famous works in this tradition is Thomas Cole’s “The Oxbow,” which depicts a sweeping, panoramic view of the Connecticut River Valley.
Also Read-
Comment on the thematic side of The Tin Flute
The Thematic Thrust Of Surfacing And The Three Broad Sections Into Which Surfacing Can Be Divided
What are the chief characteristics of twentieth century Canadian poetry
American Romanticism in Literature
American Romanticism made a significant impact on literature, producing some of the most enduring and influential works in American literary history. Here are some notable authors and their works that exemplify the spirit of American Romanticism:
- Nathaniel Hawthorne:
- The Scarlet Letter: This novel tells the story of Hester Prynne, a woman who is shunned by her Puritan community after committing adultery. Hawthorne explores themes of sin, guilt, and redemption, all set against a backdrop of the harsh, Puritanical society of 17th-century New England.
- Edgar Allan Poe:
- “The Raven”: Poe’s famous poem “The Raven” delves into the theme of grief and loss as the narrator is visited by a mysterious raven. The poem’s dark and haunting atmosphere, as well as its exploration of the human psyche, is characteristic of Poe’s work.
- Washington Irving:
- “The Legend of Sleepy Hollow”: Irving’s short story features the iconic character of Ichabod Crane and the ghostly figure of the Headless Horseman. It blends humor, folklore, and the supernatural, reflecting the Romantic interest in the mysterious and the fantastic.
- Herman Melville:
- Moby-Dick: Melville’s epic novel is a complex exploration of obsession, fate, and the human spirit. It follows Captain Ahab’s relentless pursuit of the white whale, Moby-Dick, and delves into themes of power and the unknowable forces of the natural world.
- Emily Dickinson:
- Dickinson’s poems often explored themes of love, death, and nature. Her concise and deeply emotional verses, such as “Because I could not stop for Death,” reveal her Romantic sensibilities and her fascination with the inner world of the human soul.
- Walt Whitman:
- Leaves of Grass: Whitman’s poetry collection is a celebration of the individual and the democratic spirit. His famous poem “Song of Myself” embodies the Romantic belief in the power of the self and the interconnectedness of all humanity.
American Romanticism in Poetry
In addition to the prose works, American Romanticism found a prominent expression in poetry. The following poets and their poems capture the essence of this literary movement:
- Edgar Allan Poe:
- “The Tell-Tale Heart” and “The Fall of the House of Usher” are examples of Poe’s exploration of the dark and mysterious aspects of the human psyche.
- Emily Dickinson:
- “Because I could not stop for Death”: In this poem, Dickinson personifies death as a gentle carriage driver who takes the speaker on a journey to the afterlife, reflecting her fascination with mortality and the unknown.
- Henry Wadsworth Longfellow:
- “A Psalm of Life”: Longfellow’s poem encourages readers to live purposefully and make the most of their time on Earth, echoing the Romantic emphasis on individual potential.
- Walt Whitman:
- “Song of Myself”: This epic poem celebrates the diversity of the American people and the interconnectedness of all humanity. It expresses Whitman’s belief in the importance of the individual self and the collective identity of the nation.
- James Russell Lowell:
- “The Vision of Sir Launfal”: This poem explores the themes of love and charity, highlighting the spiritual journey of the protagonist as he learns the true meaning of selflessness and compassion.
American Romanticism in Visual Arts
The influence of American Romanticism extended beyond literature and poetry into the visual arts. The Hudson River School, a group of American landscape painters, played a significant role in capturing the grandeur of the American wilderness and the sublime in nature. Some prominent artists and their works include:
- Thomas Cole:
- “The Oxbow” (1836): This painting provides a panoramic view of the Connecticut River Valley and exemplifies the Romantic fascination with the untamed American landscape.
- Albert Bierstadt:
- “Among the Sierra Nevada Mountains, California” (1868): Bierstadt’s painting showcases the stunning beauty of the American West and the idea of manifest destiny, where the expansion of the United States was seen as a divine mission.
- Frederic Edwin Church:
- “The Heart of the Andes” (1859): Church’s landscape painting captures the lush and exotic scenery of South America, emphasizing the connection between humanity and the natural world.
- Asher B. Durand:
- “Kindred Spirits” (1849): Durand’s portrait of Thomas Cole and William Cullen Bryant is a tribute to the friendship and shared ideals of the Hudson River School artists.
Conclusion
American Romanticism was a transformative and multifaceted cultural movement that emerged in response to the social, political, and economic changes of the 19th century. It celebrated the power of emotion, imagination, and individualism, while also fostering a deep connection between humanity and the natural world. This movement produced some of the most enduring and influential works in American literature, poetry, and visual arts.
Complex topics of human nature, society, and the paranormal were explored by writers such as Herman Melville, Edgar Allan Poe, and Nathaniel Hawthorne. The beauty of the American environment was depicted by artists of the Hudson River School, while poets such as Walt Whitman and Emily Dickinson exalted the individual and the connectivity of humanity. The legacy of American Romanticism is evident in its continuing influence on social and political movements, literature, the environment, and philosophy.
FAQ.
What is the difference between American Romanticism and European Romanticism?
While American Romanticism shares many characteristics with its European counterpart, it has unique elements that distinguish it. American Romanticism often focused on themes related to the American experience, such as westward expansion, the frontier, and the American wilderness. Additionally, American Romantics celebrated the democratic spirit and individualism that were seen as quintessentially American.
Who were some prominent female writers of American Romanticism?
Female authors made significant contributions to American Romantic literature. Notable figures include Emily Dickinson, Louisa May Alcott, and Margaret Fuller. Emily Dickinson, in particular, is celebrated for her innovative and deeply emotional poetry.
How did American Romanticism impact environmental awareness?
American Romanticism’s emphasis on the beauty and spiritual significance of nature played a role in the early conservation and environmental movements. Writers like Henry David Thoreau and artists of the Hudson River School helped shape the idea of preserving natural landscapes for future generations.
What are some key works of American Romantic literature that I should read?
Key works of American Romantic literature include Nathaniel Hawthorne’s “The Scarlet Letter,” Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Raven,” Herman Melville’s “Moby-Dick,” and Ralph Waldo Emerson’s essays “Self-Reliance” and “Nature.” These are excellent starting points for exploring the movement.
How did American Romanticism influence later literary movements?
American Romanticism had a profound influence on later literary movements, such as Transcendentalism, which built upon the ideas of individualism and the connection between humanity and nature. The exploration of the human psyche in works like Edgar Allan Poe’s writings also laid the foundation for psychological literature.



